How to protect your business effectively: specific measures for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Why are you particularly vulnerable?
In this era of global integration, cybercrime is an ever-growing challenge that no one can overlook. The facts and figures on this page illustrate this vividly. Small and medium-sized enterprises are particularly vulnerable. But it doesn’t have to be that way: By introducing just a few specific measures, you can take some decisive steps that will not only enhance your company’s security, but also seize new business opportunities. This brochure shows you how.
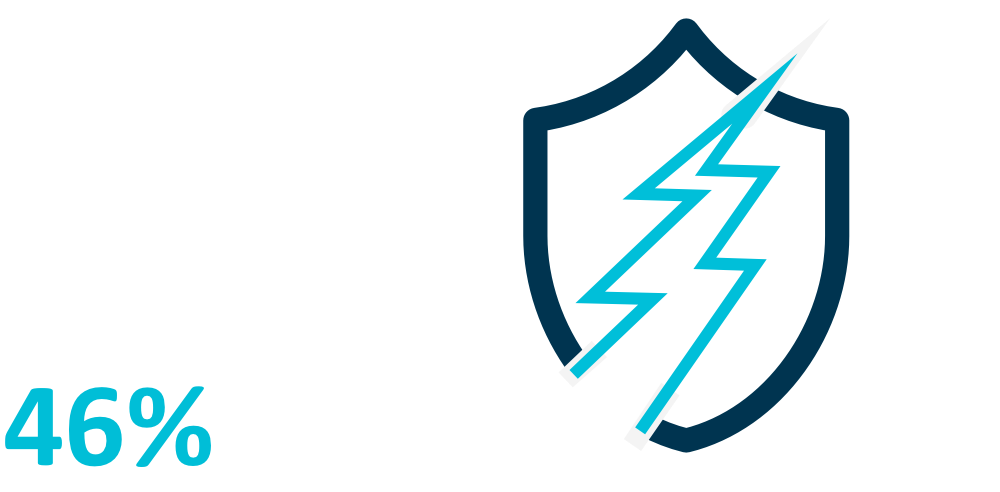



What is the role of humans?
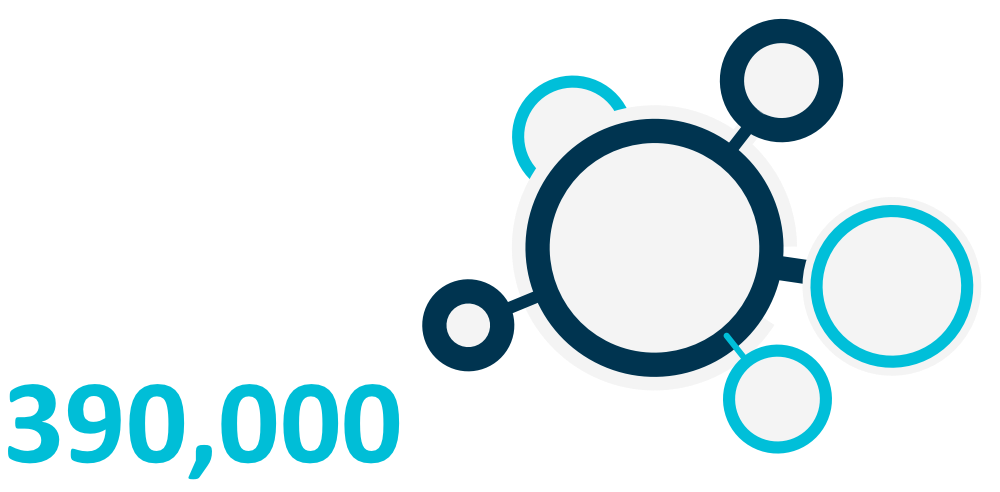
Cyberattacks launched on small and medium-sized companies in particular are generally discovered by employees. The human factor is therefore an elementary part of the process. By focusing companywide on cybersecurity, raising employee awareness levels about the issue, and providing training, you can take an action that will bolster your company’s line of cyberdefense. After all, conscious and critical behavior in the digital world creates security and trust – and that pays off. At the same time, humans will continue to present the primary gateway for cybercriminals. Carelessness can endanger your company, as the numbers on this page clearly show. Assume your responsibility and create this level of awareness. In doing so, you will take the first important step toward improving cybersecurity at your company.
How can you, as a small or medium- sized enterprise, particularly benefit from this?
As digital integration becomes more widespread, cyber- security is becoming a genuine guarantor of success. That’s because cybersecurity is not merely the response to a threat: If consistently promoted, it offers a real opportunity to enhance your own competitiveness.
Cybersecurity, when implemented systematically, creates many positive effects – especially for small and medium-sized enterprises: It ensures better reliability in your supply chains, it protects your ongoing operations, and it strengthens your trustworthiness with your customers by allowing you to handle their sensitive data responsibly. This security enhances the quality of the products and services you provide, making your portfolio more attractive and strengthening your competitive position on the markets.

You can improve your cybersecurity in three steps
Cybersecurity is a complex challenge that requires a targeted organizational, technical, and personnel-driven response. To use a sports analogy: It’s not a sprint, it’s a marathon. But even the longest journey begins with the first step.
That is why we have divided the brochure into three individual steps – which we call phases. Join us on this journey. You’ll quickly see that each individual step brings you closer to your goal.
Phase 1: Identify threats and assume responsibility
- Practice responsibility
- Heighten awareness of security risks
- Cultivate a cybersecurity culture in your organization
Phase 2: Take action and embed security
- Embed cybersecurity within the organization
- Embed cybersecurity within products and services
Phase 3: Make the structure of cybersecurity transparent, and be a role model for others
- Publish your own cybersecurity setup
- Become active – even outside your own company
You may also like
Harmonising Regulation - a CoT perspective
To read the full publication, see the download link below.

Charter of Trust Cybersecurity Policy Manifesto
Our vision is to establish a strong, secure, and resilient digital Europe that fosters innovation, economic growth, and social progress while protecting individual rights and safeguarding the values of a democratic society.




